1 Chalkboard
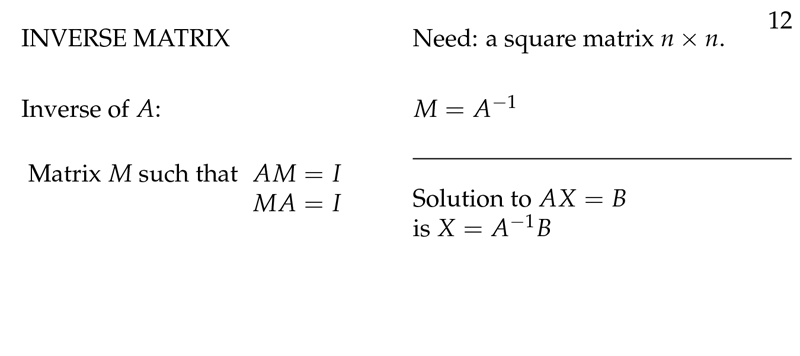
Figure 1: Inverse Matrix
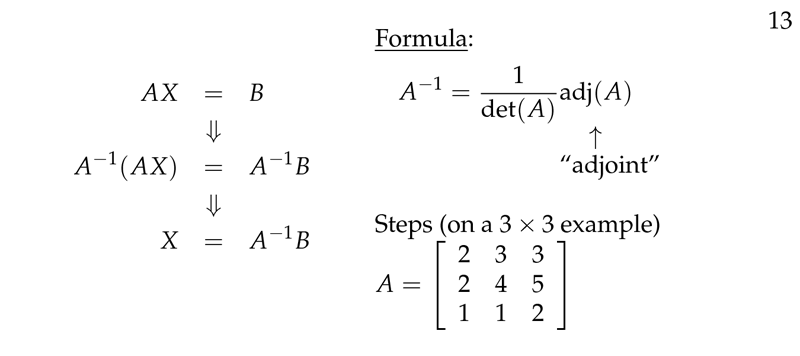
Figure 2: Inverse Matrix formula
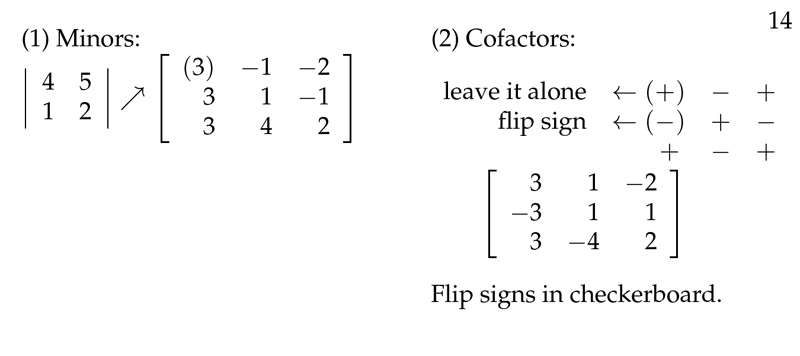
Figure 3: Inverse Matrix Formula: Minors and cofactors
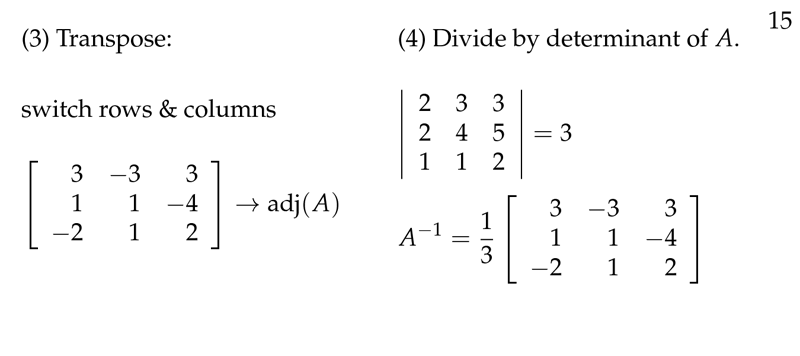
Figure 4: Inverse Matrix Formula: Transpose and Divide by \(\det(A)\)
2 How can we solve a small squared linear system?
2.1 Front
How can we solve a small squared linear system?
- Low dimensional
- \(2 \times 2\) system, or \(3 \times 3\) system
- \(x_1 = a_{11}y_1 + a_{12}y_2 + a_{13}y_{3}\)
- \(x_2 = a_{21}y_1 + a_{22}y_2 + a_{23}y_{3}\)
- \(x_3 = a_{31}y_1 + a_{32}y_2 + a_{33}y_{3}\)
2.2 Back
- Using inverse matrices
- \(A \vb{x} = \vb{b}\)
- \(A\) matrix with coefficients \((a_{ij})\)
- \({\displaystyle \vb{x} = \begin{pmatrix} x_1 \ x_2 \x_3 \end{pmatrix}}\)
- \({\displaystyle \vb{b} = \begin{pmatrix} b_1 \ b_2 \ b_3 \end{pmatrix}}\)
Solving (multiplying by inverse matrix \(M\) at the left)
\begin{align*} A \vb{x} &= \vb{b} \\\ M (A \vb{x}) &= M \vb{b}\\\ \vb{x} = M \vb{b} \end{align*}
3 When can we say that the inverse matrix of \(A\) exits?
3.1 Front
When can we say that the inverse matrix of $A$ exits?
3.2 Back
- \(M\) is the inverse matrix of \(A\)
- \(M \text{ exists } \Leftrightarrow \det(A) \neq 0\)
- That’s because of determinant law of matrix multiplication
- \(\det(AB) = \det(A) \det(B)\)
- \(MA = I \implies \det(M)\det(A) = \det(I) = 1 \implies \det(A) \neq 0\)
4 Which step do we need to calculate a matrix inverse?
4.1 Front
Which step do we need to calculate a matrix inverse?
Set \(A\) matrix, and \(A^{-1}\) as inverse matrix
4.2 Back
- \(A\) is a \(n \times n\) matrix
- \(\det(A) \neq 0\)
- Unique solution
- \(A^{-1}A = AA^{-1} = I\), Identity matrix
- \(A \vb{x} = \vb{b}\)
- \(M(A \vb{x}) = M \vb{b}\)
- \(\vb{x} = M\vb{b}\)
- \({\displaystyle A^{-1} = \frac{1}{\det(A)} \text{adj}(A) =
\frac{1}{\det(A)} \begin{pmatrix} A_{11} & A_{12} & A_{13}
\ A_{21} & A_{22} & A_{23} \ A_{31} & A_{32} & A_{33}
\end{pmatrix}^{T}}\)
- \(\text{adj}(A)\), is the adjoint or adjugate of \(A\)
- \(A_{ij} = (-1)^{i+j} \abs{A_{ij}}\) is the ij-cofactors
- \(\abs{A_{ij}}\) is the ij-minor, the determinant after remove the row \(i\) and column \(j\)
Formula steps
- Calculate the matrix of minors
- Change the signs of the entries according to the checkerboard rule
- Transpose the resulting matrix, this gives \(\text{adj}(A)\)
- Divide every entry by \(\abs{A}\)
5 What is the quick formula for inverse of \(2 \times 2\) matrix \(A\)?
5.1 Front
What is the quick formula for inverse of $2 \times 2$ matrix $A$?
\({\displaystyle A = \begin{pmatrix}a & b \ c & d\end{pmatrix}}\)
5.2 Back
- Cofactors \({\displaystyle \begin{pmatrix}d & -c \ -b & a \end{pmatrix}}\)
- adj \(A\): \({\displaystyle \begin{pmatrix}d & -b \ -c & a \end{pmatrix}}\)
- inverse of \(A\): \({\displaystyle \frac{1}{\abs{A}} \begin{pmatrix}d & -b \ -c & a \end{pmatrix}}\)
Steps:
- Switch \(a\) and \(d\)
- Change the signs on \(b\) and \(c\)
- Divide by the determinant